WHAT IS Gum Treatment?
Gum Disease also known as Periodontal Disease begins with bacterial growth in the mouth, the localized inflammation of the gingiva is initiated by bacteria in the dental plaque, which is a microbial biofilm that forms on the teeth and gingiva.
Gum treatment, also known as periodontal treatment or gum therapy, is a dental procedure aimed at addressing gum disease and maintaining the health of the gums and supporting structures of the teeth. Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, can range from mild gingivitis to more severe forms of periodontitis. Here’s an overview of gum treatment:
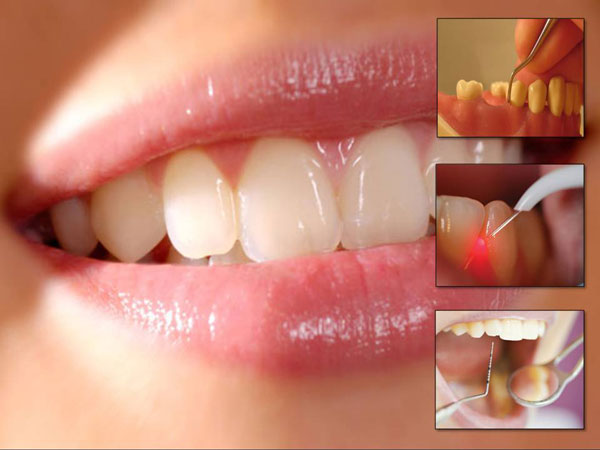
PREVENTION OF GUM DISEASE
- 1. Brush your teeth twice a day (with a fluoride toothpaste).
- 2. Floss regularly to remove plaque from between teeth.
- 3. Visit your dentist after every 6 months for a routine check-up and professional cleaning.
- 4. Quit smoking
Common Signs and Symptoms of Gum Disease:
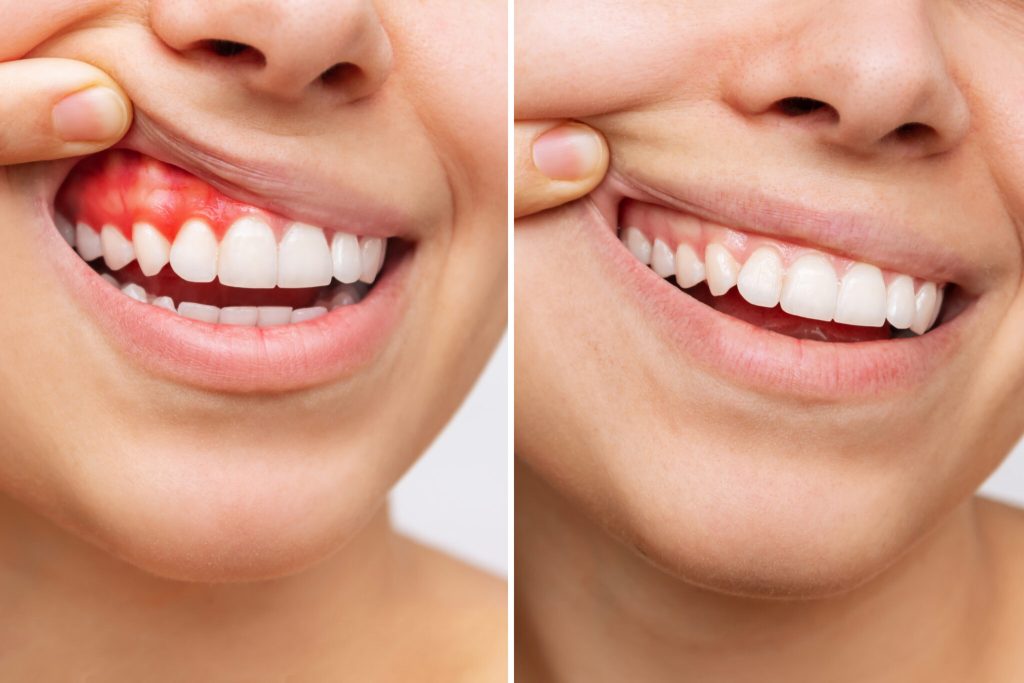
- Red, swollen, or bleeding gums, particularly when brushing or flossing.
- Persistent bad breath (halitosis).
- Receding gums, causing teeth to appear longer.
- Formation of pockets or gaps between the teeth and gums.
- Changes in tooth alignment or spacing.
- Loose or shifting teeth.
Stages of Gum Disease:
Gingivitis: This is the earliest stage of gum disease and is characterized by gum inflammation and bleeding. Gingivitis can often be reversed with good oral hygiene practices and professional dental cleanings.
Periodontitis: If gingivitis is left untreated, it can progress to periodontitis. This stage involves the formation of pockets between the teeth and gums, leading to bone loss and damage to the supporting structures of the teeth.
Gum Treatment Procedures:
Scaling and Root Planing (Deep Cleaning): This non-surgical procedure involves the removal of plaque and tartar from above and below the gumline. It also includes the smoothing of root surfaces to promote healing and prevent the accumulation of bacteria.
Pocket Reduction Surgery: In cases of advanced periodontitis, surgical procedures may be necessary to reduce the size of the pockets that have formed between the teeth and gums. This can involve lifting the gums to access and clean deeper areas of infection.
Gum Graft Surgery: In situations where gums have receded significantly, gum graft surgery can be performed to restore gum tissue by taking grafts from another part of the mouth or using donor graft material.
Laser Therapy: Some dental professionals use lasers to remove infected tissue and stimulate healing in the gums.
Maintenance and Prevention:
- Regular dental check-ups and cleanings are crucial to monitor and maintain gum health.
- Good oral hygiene practices, including regular brushing, flossing, and using an antiseptic mouthwash, are essential to prevent gum disease.
- Smoking cessation is important, as smoking is a significant risk factor for gum disease.
Benefits of Gum Treatment:
- Halt the Progression of Gum Disease: Gum treatment can stop the progression of gum disease and prevent further damage to teeth and supporting structures.
- Improved Oral Health: Healthy gums are essential for overall oral health and can help prevent tooth loss and other dental problems.
- Enhanced Aesthetics: Treating gum disease can improve the appearance of the smile by addressing issues such as receding gums and tooth spacing.
Gum treatment is a critical aspect of maintaining oral health and preventing the advancement of gum disease. Early detection and intervention are key to effective gum therapy. It is essential to consult with a dentist or periodontist for an accurate assessment and appropriate treatment plan if you suspect gum disease or are experiencing any symptoms related to gum health.
